Standard Operating Procedure
1. Raising a Ticket (Issue)¶
- Identify a Problem or Feature
- Detect a bug, improvement, or new feature idea for Tevico Community.
- Search the Tevico Issues to avoid duplicates.
-
Create an Issue
- Go to the Tevico’s Issues tab.
- Click "New Issue".
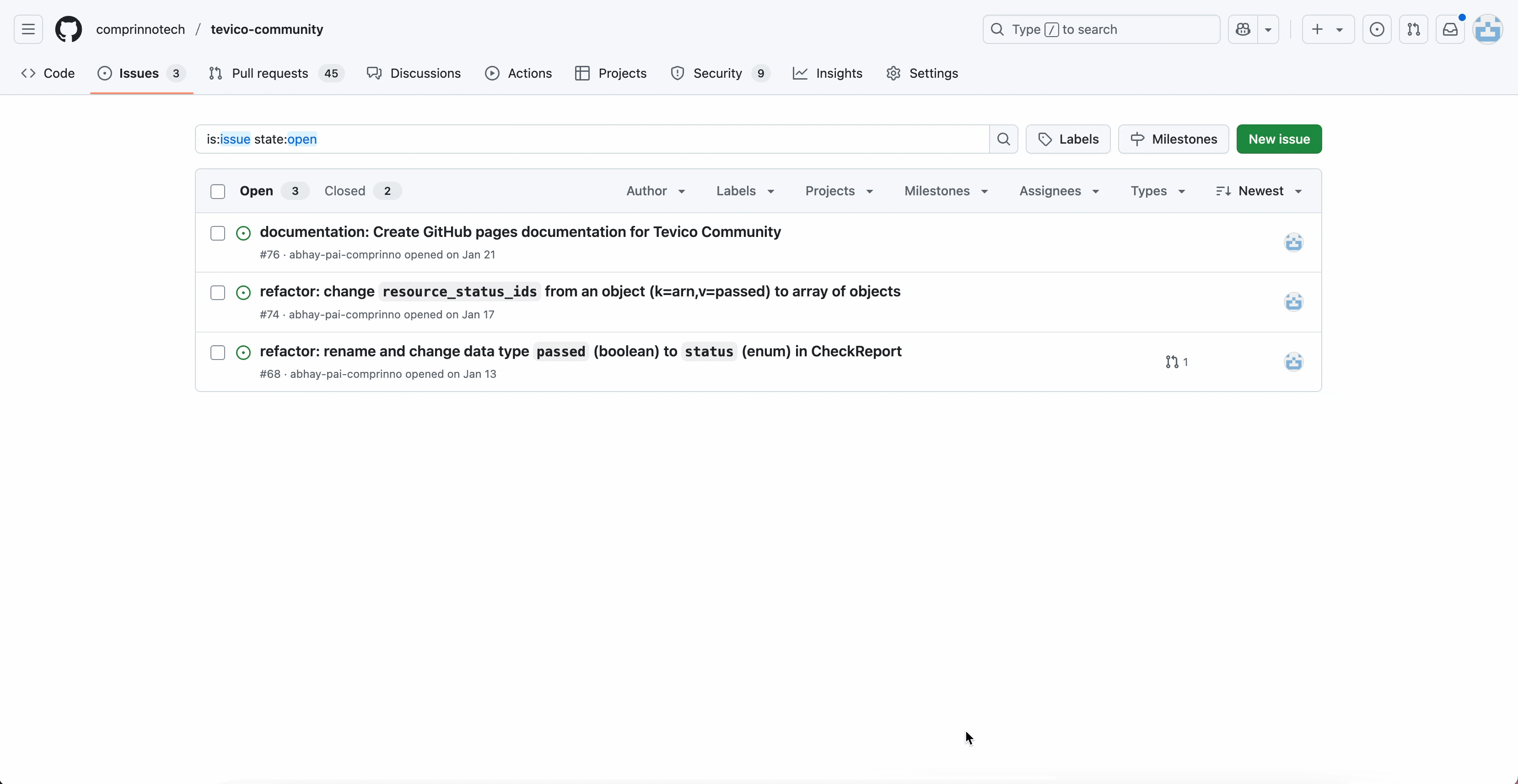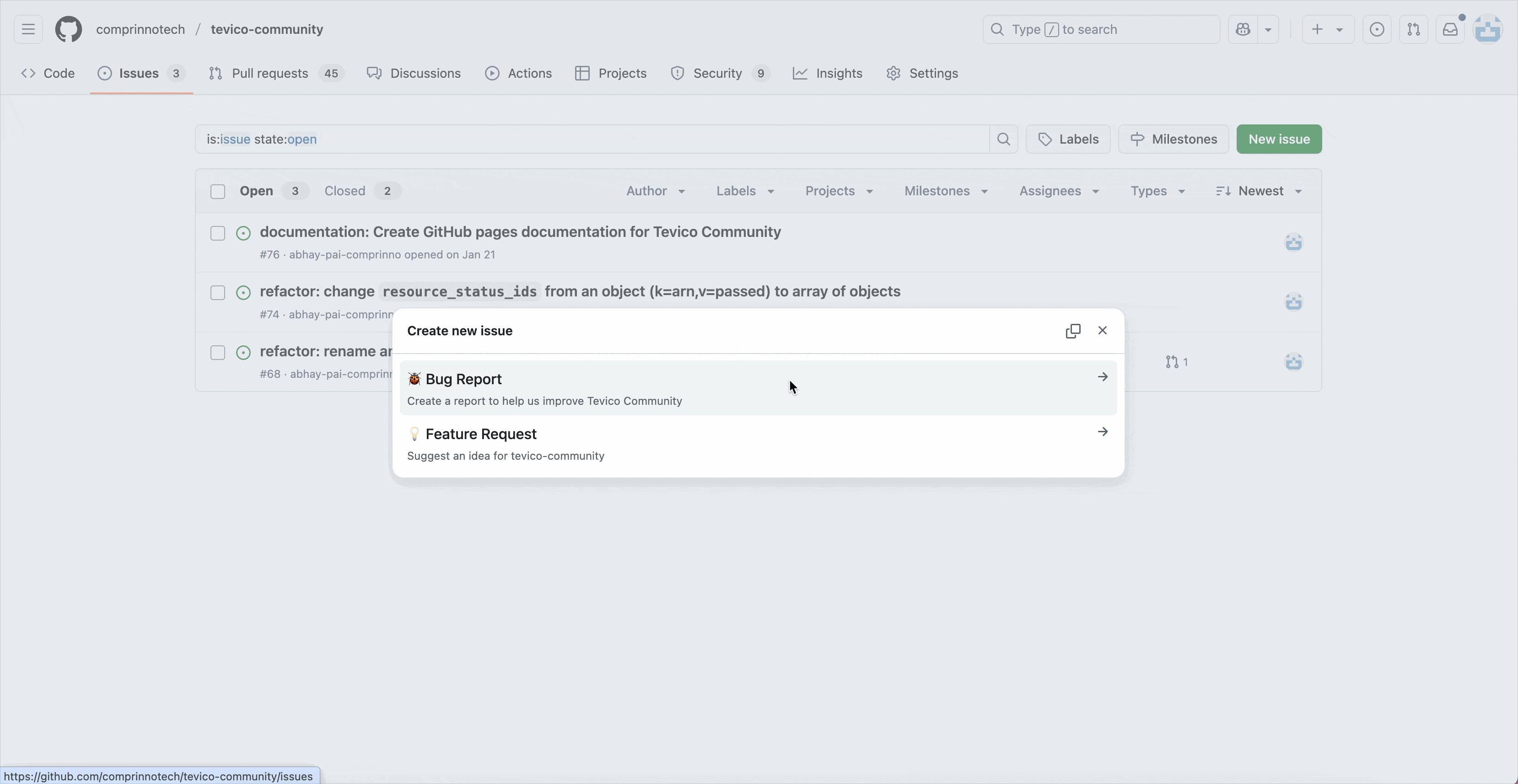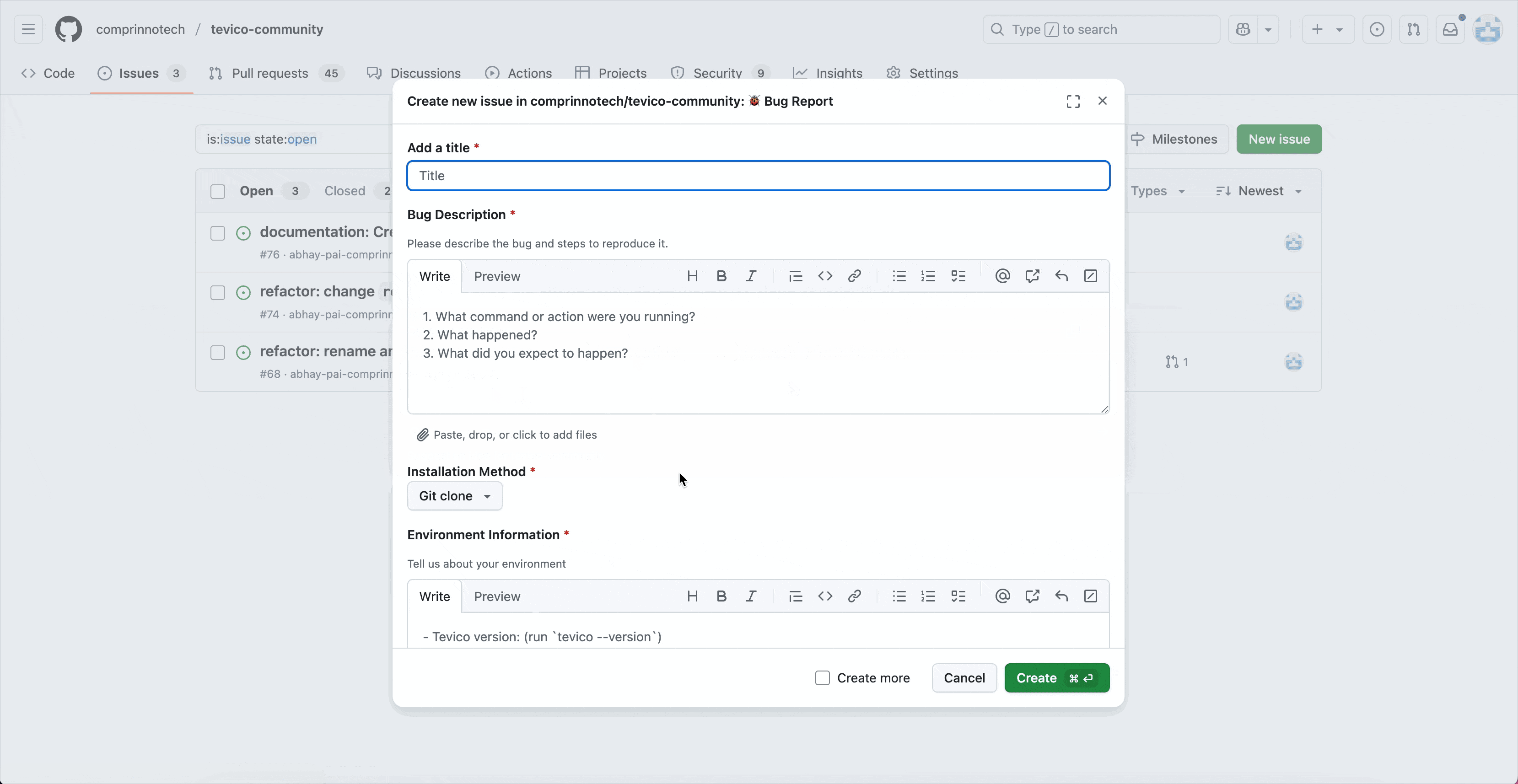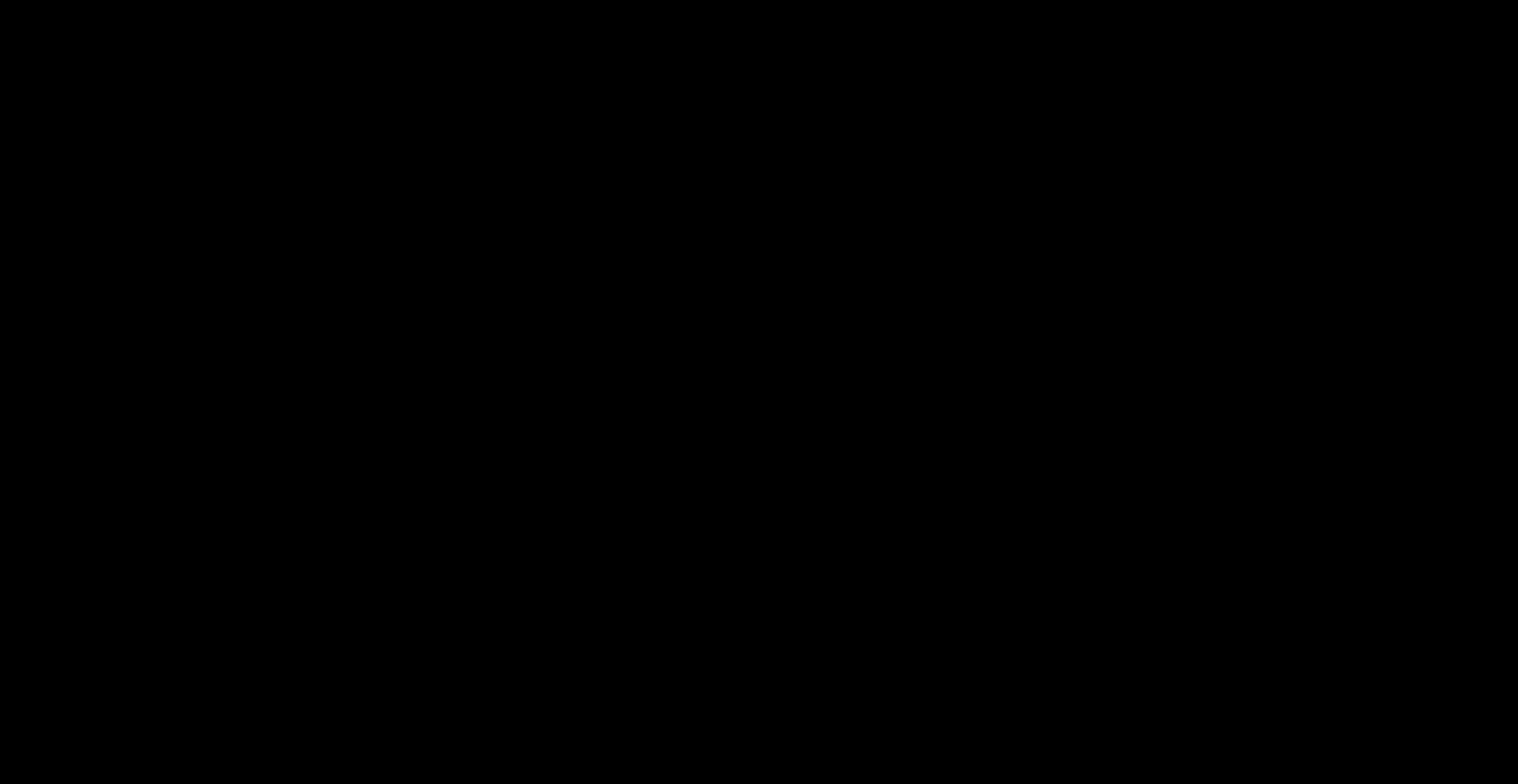
- Select the appropriate template (bug, feature, etc.).
- Fill in required details:
- Title: Concise description.
- Description: Detailed information, steps to reproduce (if bug), screenshots, etc.
- Submit the issue.
-
Issue Triage
- Project maintainers review the issue.
- The issue may be labeled, assigned, or discussed further.
2. Forking and Cloning the Repository¶
-
Fork the Repository
- Click the "Fork" button at the top right of the repo page.
- This creates a copy under your GitHub account.
-
Clone Your Fork
- Copy your fork’s URL.
- In your terminal:
- Navigate into the cloned directory:
3. Creating a Branch¶
-
Sync with Upstream
- Add tevico as an upstream remote:
- Fetch latest changes:
-
Create a Feature/Issue Branch
- Name your branch descriptively, e.g.,
fix/issue-123-bug-descriptionorfeature/new-login-ui: - OR you can create a Branch Directly from GitHub
- Navigate to the issue page on the GitHub repository.
- Click the "Create a branch" link in the right sidebar.
- Choose your fork as the repository (if prompted).
- Accept or modify the suggested branch name.
- Click "Create branch" to generate the branch.
- Pull the new branch to your local repository:
- Name your branch descriptively, e.g.,
4. Development¶
-
Make Code Changes
- Implement your fix or feature.
- Regularly commit your work with clear messages:
- Follow commit message best practices:
Where
typeis one of: feat, fix, docs, style, refactor, test, chore
-
Test Your Changes
- Run existing and new tests to ensure code quality.
-
Keep Your Branch Updated
- Periodically pull from the upstream main branch:
- Resolve any merge conflicts.
5. Push and Create Pull Request¶
-
Push Your Branch
- Push your changes to your fork:
-
Create a Pull Request (PR)
- Go to the original repository on GitHub.
- Click "Compare & pull request".
- Fill out the PR form:
- Link the Issue: Use
Closes #123to auto-close the issue on merge. - Describe Your Changes: Summarize what and why.
- Link the Issue: Use
- Submit the PR.
6. Code Review & Iteration¶
- Engage in Review
- Respond to feedback from maintainers and reviewers.
- Make additional commits as needed.
7. Merging¶
-
Approval
- Wait for reviews and approvals as per project policy.
-
Merge
- Maintainers (or you, if permitted) merge the PR.
- The issue is closed automatically if linked.
-
Cleanup
- Delete your feature branch remotely and locally: